Remove the plants in an area measuring 0.1 m² (about 12" square), beat them on to a clean surface and count the number of larvae (Fig. 1) dislodged from the plant. Repeat this procedure at least in five locations in the field to get an accurate count.
 |
| Figure 1. Diamondback larva measuring ~8mm long. Note brown head capsule and forked appearance of prolegs on posterior. |
 |
| Figure 2. Diamondback moth pupa within silken cocoon. |
Economic threshold for diamondback moth in canola at the advanced pod stage is 20 to 30 larvae/ 0.1 m² (approximately 2-3 larvae per plant). Economic thresholds for canola or mustard in the early flowering stage are not available. However, insecticide applications are likely required at larval densities of 10 to 15 larvae/ 0.1 m² (approximately 1-2 larvae per plant).
More information about Diamondback moths can be found by accessing the pages from the new "Field Crop and Forage Pests and their Natural Enemies in Western Canada: Identification and Field Guide". View ONLY the Diamondback moth page but remember the guide is available as a free downloadable document as both an English-enhanced or French-enhanced version.
Reminder - Pheromone traps attracting male Diamondback moths (Fig. 3) have been deployed across the prairies.
 |
| Figure 3. Diamondback moth. |
Across the prairies, provincial staff coordinate diamondback pheromone trapping during the growing season:
● Counts will be reported by the provincial staff in Saskatchewan.
● Manitoba Agriculture and Rural Initiatives posted low DBM counts which can be reviewed here.
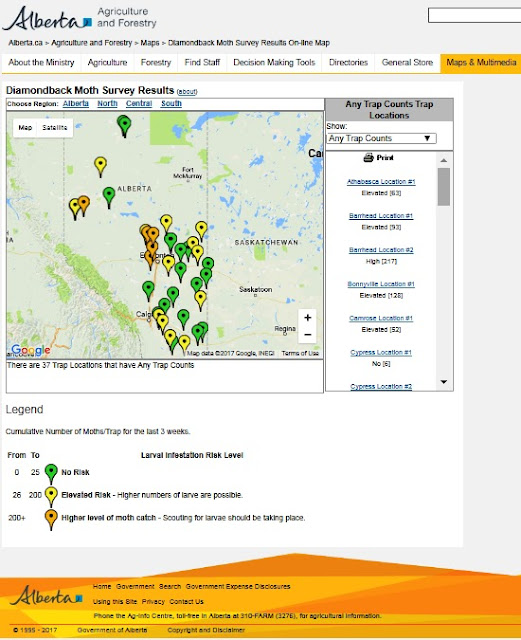
● Alberta Agriculture and Forestry has a live 2016 map reporting Diamondback moth pheromone trap interceptions. A copy of the map (retrieved July 20, 2017) is below for reference.