As of July 2, 2018, the predictive model output indicated that the average instar = 3.7, with 1st instar (5%), 2nd (12%), 3rd (24%), 4th (34%), 5th (23%), and 2.4% in the adult stage. The most rapid development occurred across southern MB and southeast SK (Fig. 1).
 |
| Figure 1. Grasshopper development (average instar stage) based on model simulations for April 1-July 2, 2018. |
Model output for Saskatoon illustrates that populations are primarily in the 4th and 5th instars with appearance of a few adults (Fig. 2). By comparison, model output based on long-term climate data indicates that grasshopper populations should on average only be in the 3rd and 4th instars (Fig. 3).
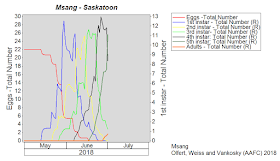 | ||
| Figure 2. Predicted grasshopper phenology at Saskatoon SK. Values are based on model simulations for April 1-July 2, 2018. |
 |
| Figure 3. Predicted grasshopper phenology at Saskatoon SK. Values are based on model simulations for Long Term Climate Normals. |
● Compare counts to the following damage levels associated with pest species of grasshoppers:
0-2 per m² - None to very light damage
2-4 per m² - Very light damage
4-8 per m² - Light damage
8-12 per m² - Action threshold in cereals and canola
12-24 per m² - Severe damage
>24 per m² - Very severe damage
* For lentils at flowering and pod stages, >2 per m² will cause yield loss.
* For flax at boll stages, >2 per m² will cause yield loss.
Biological and monitoring information related to grasshoppers in field crops is posted by Manitoba Agriculture, Saskatchewan Agriculture, Alberta Agriculture and Forestry, the BC Ministry of Agriculture and the Prairie Pest Monitoring Network. Also refer to the grasshopper pages within the new "Field Crop and Forage Pests and their Natural Enemies in Western Canada: Identification and management field guide" as an English-enhanced or French-enhanced version.